Innovation is a Mindset
My Approach
Start by listening and observing for better understanding. Frame questions to inspire change. Remember to let go of judgment, as everything is subjective. Strive to rid clutter and capture the "essence" of a subject matter. Use design thinking to create experiences that drive impact.

UNDERSTAND
Study and learn from the real and concrete world by observing people's behavior, understanding needs wants, and wishes.
DESIRABILITY
Use knowledge to extract insights and frame new questions that inspire opportunities that serve unmet needs.
Empathize
Conduct research to develop an understanding of the subject matter.
Define
Frame “How might we...” questions to define opportunities.
EXPLORE
Create as many ideas as possible that address solutions to newfound challenges. No idea is too silly. Aim for quantity.
FEASIBILITY
Consider each ideas’ feasibility, focus on one conversation at a time and choose the best ideas to explore deeper.
Ideate
Generate lots of ideas to offer options of focus for each topic.
Prototype
Build tangible, tactile prototypes of ideas to learn experientially.
MATERIALIZE
Narrow the focus based on feedback from users and begin to refine the details of each selected opportunity.
VIABILITY
Refine the idea by getting user feedback and share each improvement. Iterate details until they feel right.
Test
Engage with users to test ideas and prototypes for feedback.
Share
Craft and share the story to introduce the right ideas to users.
Tools for Innovation
Design thinking is a framework and process, it provides tools that can help gain clarity. The mindset embraces ambiguity and gives it structure.

Where Innovation is born
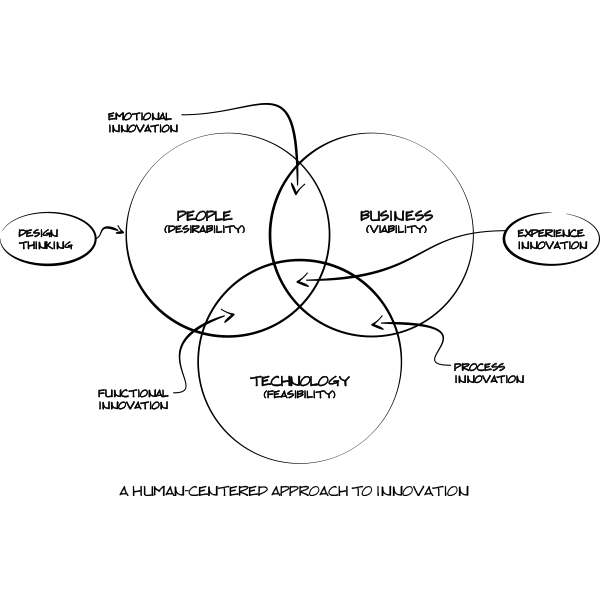
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation. It brings together what is desirable from a human point of view with what is technologically feasible and economically viable. It's a methodology to address a vast range of challenges.

How opportunities are identified
Design thinking is a flexible approach to explore opportunities and define challenges. It uses divergent thinking to broaden your scope to see the larger picture and convergent thinking to narrow in on the essence of the challenges and opportunities identified.

Where solutions are formed
Design thinking is a process of how solutions form. It starts by being inspired to solve a particular problem, then progresses to generating lots of different ideas, no matter how silly, and ends with implementing ideas in the real world to test and refine. A simple framework that often isn't linear, allowing you to iterate and jump between them until a solution appears.

Where value emerges
Design thinking is about being human-centered. It starts by understanding that all challenges and problems are human. Immerse yourself in people's worlds. Listen carefully to what people say, how people think, what people do, and how people feel about the issues and problems. This insight will inform and depict how or what challenges are worth solving.

How offerings are framed
Design thinking tools can help frame the position of new and existing offerings to assess their impact and measure the value of ideas against a broader market. They help identify how ideas fit against existing offerings to learn how a new offering is perceived.

How ideas come to life
Design thinking is a process to learn from failure. Iteration is the art of the pivot. By building and getting feedback quickly, you can refine and build stronger. Iterate, iterate, iterate again.
How the journey feels
The journey of human-centered design is similar to that of an entrepreneur. You tinker and you test, fail early and often and spend lots of time not knowing the answer to the challenge at hand. And yet, still, forge ahead. By being an optimist and a maker, experimenter, and learner, you empathize, and iterate, and look for inspiration in unexpected places. With the belief that a solution is out there, by keeping focused on people and their challenges, asking the right questions, and eventually, you get there. You dream up lots of ideas, some that work and most that don’t. You make your ideas tangible to test and refine. In the end, the approach is tenacious and eventually produces solutions you’d never dreamed of when you started.
By trusting the entrepreneur's optimism and adopting design thinking, a new mindset emerges that sets you apart.
Design thinking is a tool for everyone, it embraces ambiguity and gives it structure.

Design + Venture
The design thinking framework is a mindset that turns questions into opportunities and opportunities into ventures. The inherent value of a product or service is that it makes a persons' life easier (functional innovation), a person has a positive emotional engagement (emotional innovation), and pushes the boundaries of how its made and how it gets in the hands of consumers (process innovation). In the end, the solution (experience innovation) is born from the intersection of desirability, viability, and feasibility.
I work with people who seek to innovate and companies that want to stand apart.
Reach out if you’d like to collaborate.
© ENDRIT HAJNO INC. 2021. All Rights Reserved.